
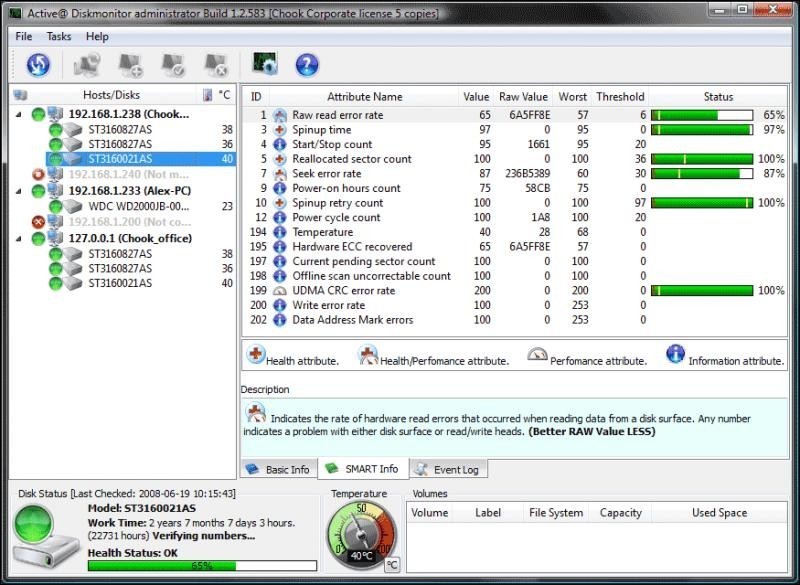
Windows also maintains its own health monitoring state for storage, which can be queried using the Get-PhysicalDisk cmdlet in PowerShell Get-PhysicalDisk Get-WmiObject -namespace root\wmi –class MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus Drive Health Status We can integrate these values using the MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus class in the root\WMI namespace This is equal to 1825 days in 24/7 mode or 43800 hours.” On some pre-2005 drives, this raw value may advance erratically and/or “wrap around” (reset to zero periodically). “By default, the total expected lifetime of a hard disk in perfect condition is defined as 5 years (running every day and night on all days). The raw value of this attribute shows total count of hours (or minutes, or seconds, depending on manufacturer) in power-on state. If this attribute is decreasing, it is a sign of problems in the mechanical subsystem.Ĭount of hours in power-on state. For some drives, this number may increase during normal operation without necessarily signifying errors.Īverage performance of seek operations of the magnetic heads. The raw value has different structure for different vendors and is often not meaningful as a decimal number. Such a failure may be due to numerous factors, such as damage to a servo, or thermal widening of the hard disk. If there is a partial failure in the mechanical positioning system, then seek errors will arise. (Vendor specific raw value.) Rate of seek errors of the magnetic heads. The function of this attribute is not specified. This value is primarily used as a metric of the life expectancy of the drive a drive which has had any reallocations at all is significantly more likely to fail in the immediate months. The raw value represents a count of the bad sectors that have been found and remapped. Thus, the higher the attribute value, the more sectors the drive has had to reallocate. The spindle turns on, and hence the count is increased, both when the hard disk is turned on after having before been turned entirely off (disconnected from power source) and when the hard disk returns from having previously been put to sleep mode.Ĭount of reallocated sectors.
If the value of this attribute is decreasing there is a high probability that there is a problem with the disk.Īverage time of spindle spin up (from zero RPM to fully operational ).Ī tally of spindle start/stop cycles. Overall (general) throughput performance of a hard disk drive. For some drives, this number may increase during normal operation without necessarily signifying errors. (Vendor specific raw value.) Stores data related to the rate of hardware read errors that occurred when reading data from a disk surface.
MONITOR HARD DISK HEALTH SOFTWARE
When an anomaly is detected, a corresponding error code is set which can then be read by software or other means to warn you that something isn’t quite right with your hard disk.īelow are a sample list of failures errors (source S.M.A.R.T. The Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology feature that is built into most hard disks today, is a self monitoring system that allows the disk to report on predicted and determined anomalies during normal operation. Lets take a look at each of these in isolation first.
There are several ways with modern machines that we can monitor hard disk health, from in-built SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) errors, do read error counts, and through to wear values, with most values readily available to query via WMI. The trouble of course is how do we monitor for signs of a disk failure and more importantly, how can we be proactive about replacing hardware before something goes to the scrap heap. Of course today SSD’s are common place so a lot of you might be thinking, what is he on about, but if you ask those around in IT long enough, they will tell you stories of how the impending sound of doom when your hard disk starts to fail. We have all been there, you are working away fine and then you hear the unmistakable tick tick tick sound of a failing hard disk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
